.jpg)
During the MPOX outbreak at 2022 the Case fatality rate (CFR) was below 0.1%.
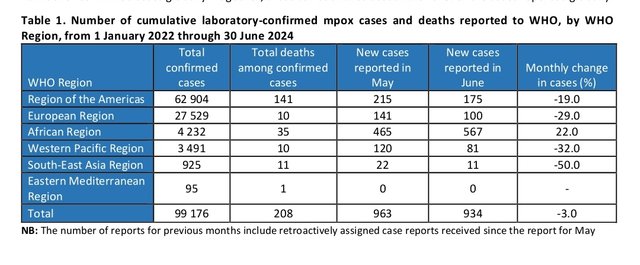
Now with the Clade 1b the case fatality rate of MPOX has significant increased to 3-4% among all MPOX cases at Africa. ECDC has now warned within a bulletin to healthcare workers about the high risk of death by MPOX infection at immunecompromised and HIV infected patients - especially those which are starting an antiviral therapy against HIV and developing an IRIS Syndrom when the immunsystem of these patients starts to restore its immuncompetence after starting its antiviral therapy.
A 15% mortality rate was described among individuals with advanced HIV-related disease characterised by CD4 cell counts below 200 cells per mm3 [43]. An immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) to mpox was suspected in 21 (25%) out of 85 people who were initiated or re-initiated on antiretroviral therapy (ART), of whom 57% died. ECDC
More than 57% mortality at the Clade 2 infected population was oberserved. From my point of view this Case fatality rate will rise at the patient subpopulation in case of Clade 1b infection up to nearly 90% if the immunsystem restarts during an MPOX Infection.
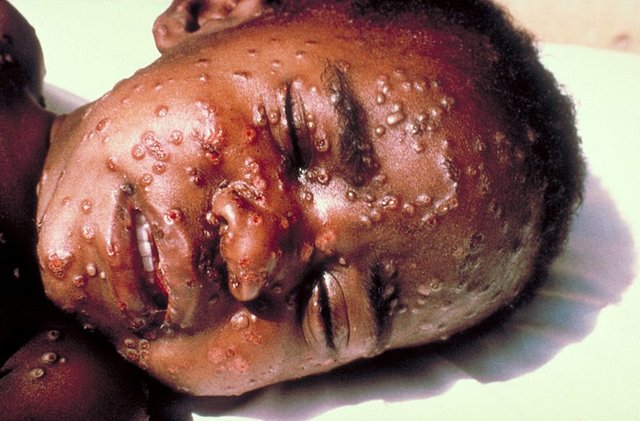
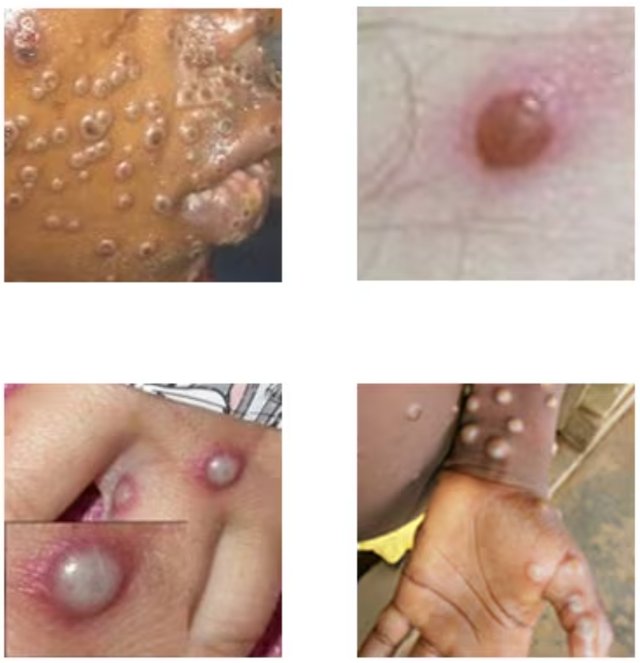
While Clade 2 normally has less than 20 skin lessions, the new clase 1b is able to develope more than 100 skin lessions which are able to occur at the palm of the hands and feets - very painful and combined with pruritus in the deeper parts of the skin. Scrathing effects can lead to bacterial superinfections resulting in more severe disease course.
Beyond severe infections of the eye - called MPXROD - even pneuomonia, encephalitis and genital ulcer - especially at immuncompromised inviduals were observed at the clase 1b MPOX cases.
High risk if severe disease also excist at childs below age of 10 and pregnant woman.
Sexual transmission of MPOX virus has been described up to 12 weeks after infection.
Animal to human is further a concern about transmission of the highly contagious MPOX Virus.
Further information is available at ECDC - Link